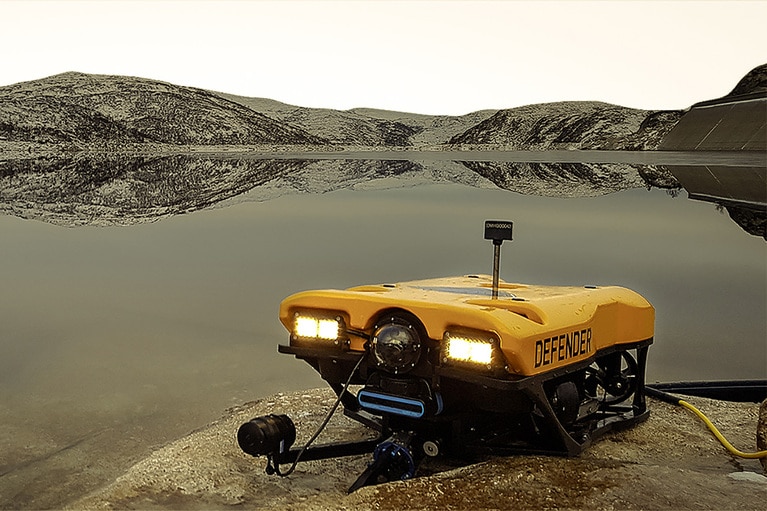
VideoRay drives safe, effective underwater exploration leveraging AI and today’s newest technologies
Vicor Powering Innovation podcast discusses the proliferation of ROV applications and how VideoRay is responding to new underwater missions
Robotics solutions and case studies
Case study: Wireless battery charger
As robotic fleets reshape logistic, delivery and inspection industries the demand for more efficient and flexible charging solutions is increasing. At the same time more autonomy requires the elimination of human intervention. Targeted at aerial, mobile, marine and industrial robots this customer, WiBotic, wanted to develop a wireless charging station that avoided unreliable mechanical connectors and intelligently adjusted its output to meet the needs of different robots’ onboard batteries. The key goals were:
An external AC supply provided the nominal 48V power to the charging station. The voltage varied due to losses in the long cable, which a PRM buck-boost module then regulated. The output voltage and current of the PRM could be varied to match the wide range of battery types of the visiting robots. Key benefits were:
A PRM buck-boost module regulated the widely varying input voltages, providing a precisely regulated output, adjustable over a wide range to suit each robot’s battery requirement. To analyze this power chain go to the Vicor Whiteboard online tool.

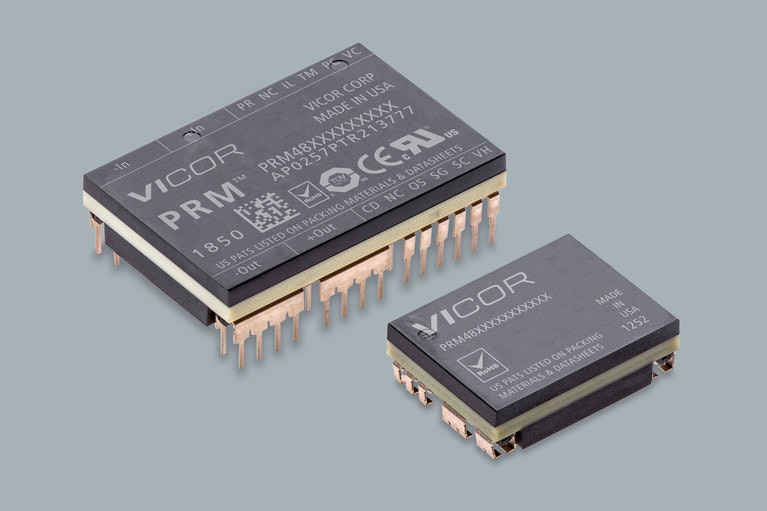
PRM pre- and post-transformation regulators
Input: 48V (36 – 75V)
Output: 48V (5 – 55V)
Power: Up to 600W
Efficiency: Up to 97%
As small as 22.0 x 16.5 x 6.73mm
VideoRay drives safe, effective underwater exploration leveraging AI and today’s newest technologies
Vicor Powering Innovation podcast discusses the proliferation of ROV applications and how VideoRay is responding to new underwater missions
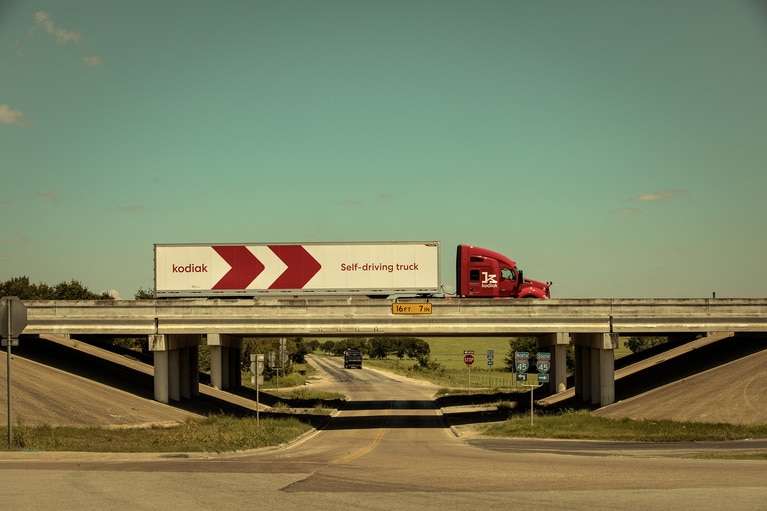
The future of long-haul trucking is accelerating autonomously on a freeway near you
Kodiak autonomous technology revolutionizes long-haul trucking. Learn more about Vicor power modules that drive mission critical ‘seeing’ sensors
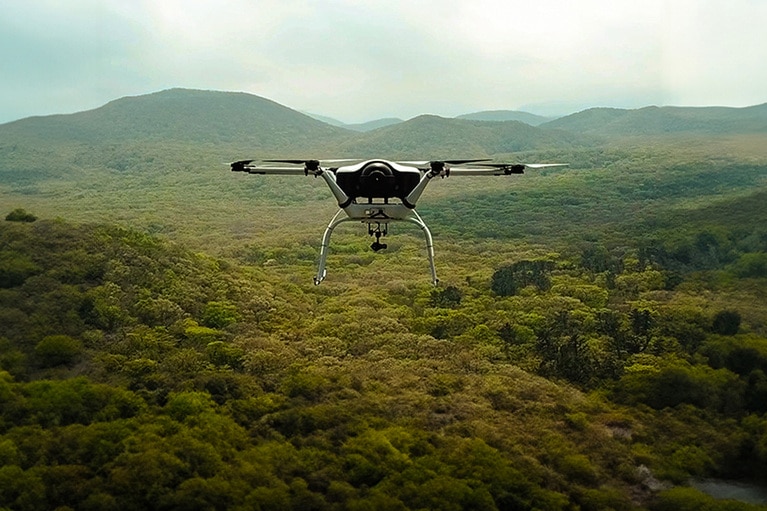
Next generation hydrogen powered drones are doing search and rescue, saving lives
Doosan Mobility’s life-saving drones using hydrogen fuel cells and high-density power modules, enabling 5x longer flight time than lithium ion batteries
From toys to construction site tools, OLogic brings robotic ideas to life
OLogic extols high-density power modules to drive today’s robotic revolution