Accelerate your move to a high performance 48V power delivery network
This eBook provides guidance on designing 48V power delivery networks to enhance the performance, efficiency, and reliability of industrial products
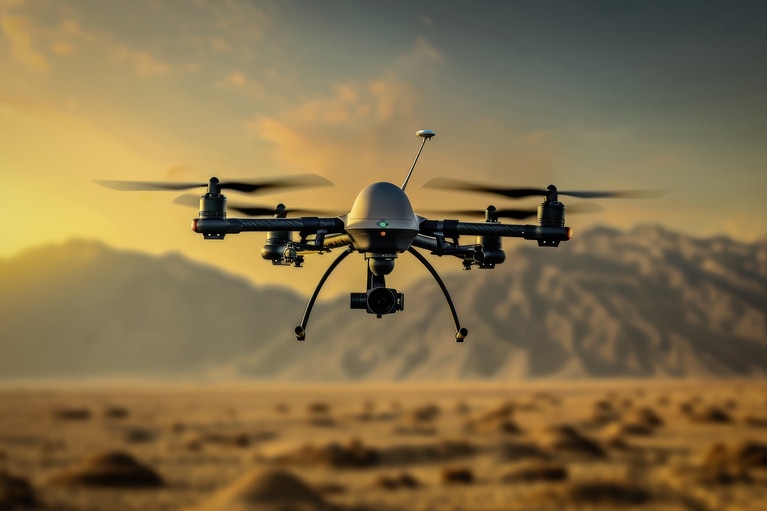
Inspection UAVs ensure that infrastructure is sound, safe, and functional. These UAVs must be able to be easily maneuvered and nimbly access hard- to-reach spaces to inspect vast terrains. To succeed in their mission, they must also operate reliably in harsh environments and withstand electrical interference from power lines and other high-energy sources. The key goals were:
Vicor high-efficiency and high-performance power modules enable inspection UAVs to minimize size and weight to maximize the sensor payload required to perform the actual inspection. With enough power and high efficiency, they allow for an agile UAV with increased flight time, even in harsh environments.

High-power density to enable smaller form factor and lower weight

Minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI)

ZVS topology enables modules with up to 98% efficiency
Power dense Vicor DCMTM DC-DC converters and ZVS Buck and Buck-Boost regulator modules are ideal for inspection UAVs. The compact DCM delivers enough power to the motors, while the Buck and Buck-Boost regulators operate with a wide input range to allow loads to be powered by the full range of the battery, providing a reserve for safe landing and recovery. The compact modules allow for the use of a smaller magnetic shield, thereby reducing that weight in addition to the weight savings of the Vicor modules.
電力供給ネットワーク(PDN)

非絶縁 レギュレータ
入力電圧: 12V (8 – 18V), 24V (8 – 42V), 48V (30 – 60V)
出力電圧: 2.2-16V
出力電流: 最大22A
ピーク効率: 98%
10.0 x 10.0 x 2.56mm 他
Accelerate your move to a high performance 48V power delivery network
This eBook provides guidance on designing 48V power delivery networks to enhance the performance, efficiency, and reliability of industrial products
Build better UAVs using modular power
Power Delivery Networks (PDN) based on Vicor high performance power modules enable innovative designs for the next generation of UAV development
High-efficiency, high-density modules free up space for advanced communications and extend range
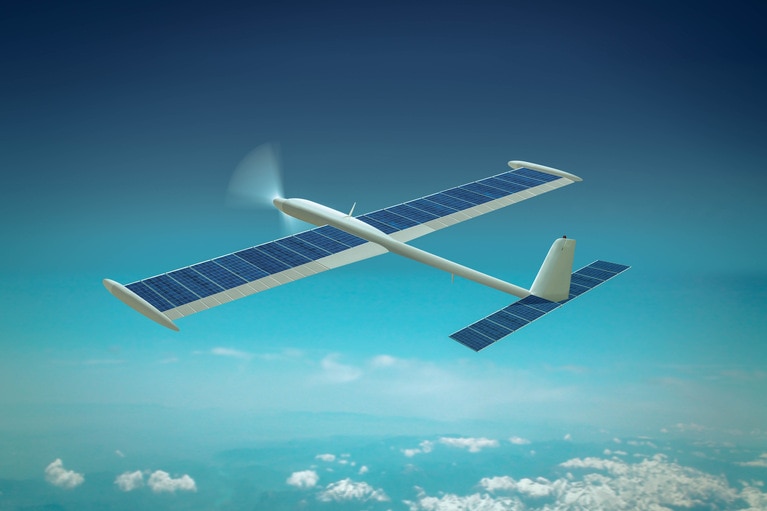
High-efficiency class of UAV depend on solar power to meet its long flight time requirements
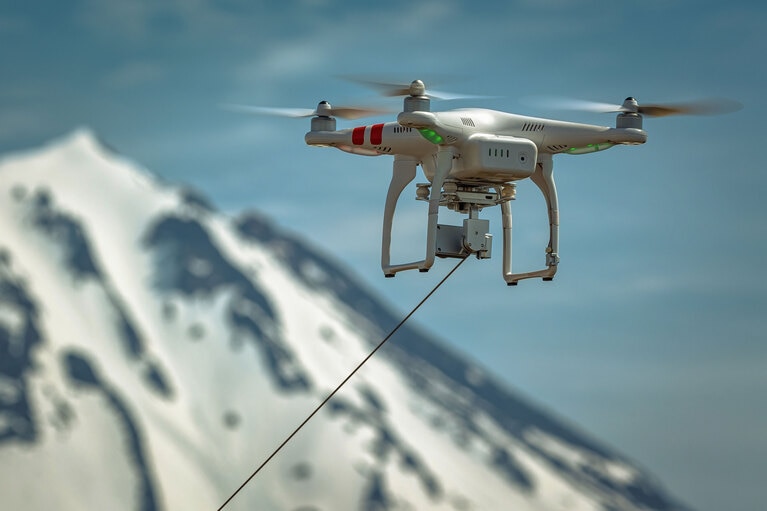
High-density, high-power modules enable lighter, safer, lower cost tether cables to extend missions
This class of unmanned vehicle is powered and controlled via a tether from a ground-based power source assisting in extended missions